von Dr. Roland Mildner (alpha 6/1983, S. 140)
Kurzlösung
Waagerecht:
3) 13;
4) 11;
6) 12;
8) 14;
9) 1111;
10) 10;
11) 13;
13) 52;
15) 15;
16) 30;
17) 41;
18) 1615;
19) 12;
21) 15;
22) 100;
23) 764;
25) 17;
26) 40;
27) 128;
29) 09;
30) 17;
32) 25;
33) 10;
34) 10;
35) 16;
37) 1251;
40) 6000;
41) 81;
43) 90;
44) 91;
46) 12;
47) 11;
49) 10;
50) 24;
53) 74;
54) 45;
56) 40;
58) 90;
59) 83;
61) 32;
62) 18;
63) 60.
Senkrecht:
1) 13;
2) 11;
3) 121;
5) 144;
7) 210;
8) 111;
12) 385;
14) 2301;
15) 1245;
20) 21;
21) 10;
23) 77;
24) 44;
27) 19500;
28) 8110;
29) 02;
31) 70;
34) 181;
36) 6450;
37) 16;
38) 2048;
39) 10;
42) 100;
43) 999;
45) 10;
46) 111112;
48) 10;
51) 54;
52) 14;
53) 7104;
55) 5100;
57) 01;
58) 99;
60) 362880;
61) 31.
Ausführliche Lösung
Waagerecht:
3) f(4,5) = 3,5 ⋅ 4,5 - 2,75 = 13 ;
4) 0,5x - 5,5 = 0 → x = 11 ;
6) 5x + y - 12 = 0 und x = 0 → y = 12 ;
8) y = 14x + 3/2 → m = 14 ;
9) y = x - 1109 = 2x/1111 → x = 1111 ;
10) x ≥ 0 → 1,4x + 1 = x + 5 → x = 10 ;
11) 6x - 6 = 2x + 46 → x = 13 ;
13) (4x - 8)/20 = 10 → x = 52 ;
15) Gerade (Zweipunktegleichung): x - 15y - 15 = 0, für y = 0 ergibt sich x = 15 ;
16) x/2 + x/3 - x/5 = 19x/30 = 19 → x = 30 ;
17) (x - 5) ⋅ (x + 14) = (x + 3) ⋅ (x + 4) → 2x = 82 → x = 41 ;
18) x/19 - 17 = 68 → x = 1615 ;
19) x2 - 11x - 12 = 0 → x1 = 12 (x2 = - 1) ;
21) y - 57 = x2 - 14x = (x - 7)2 - 49 → y - 8 = (x - 7)2 → S = (7, 8) → Summe = 7 + 8 = 15 ;
22) x0 = 2 → f(2) = 102 = 100 ;
23) x3 - 28x2 + 259x - 792 = (x - 8)(x - 9)(x - 11) = 0 → x1 = 8, x2 = 9, x3 = 11 →
Differenz = x1x2x3 - (x1 + x2 + x3) = 792 - 28 = 764 (Einfacher: Nach dem Vietaschen Wurzelsatz Produkt und Summe der Nullstellen sofort aus dem Funktionsterm f(x) ablesen.) ;
25) x2 - 17x + 72 = (x - 9)(x - 8) = 0 → x1 = 9, x2 = 8 → x1 + x2 = 17 (Einfacher: Nach dem Vietaschen Wurzelsatz Summe der Nullstellen sofort aus dem Funktionsterm f(x) ablesen.) ;
26) a = sin(&pi/2) + ln(e3) + (log0,5(1/64))2 = 1 + 3 + 36 = 40 ;
27) a = 230, b = 223 → c = a/b = 27 = 128 ;
29) Setze ex = a und log3y = b: 2a + b = 4 und 5a + 6b = 17 → a = 1 = ex, b = 2 = log3y → x = 0, y = 9 → (x, y) = (0, 9), Schreibweise
09 ;
30) 2ex-17 = lg(102) = 2 → ex-17 = 1 → x - 17 = 0 → x = 17 ;
32) log3(3log3(log5(x1/2))) = log3(log5(x1/2) = log31 = 0 → log5(x1/2) = 1
→ log5x = 2 → x = 52 = 25 ;
33) Setze lgx = y → y2 + 3y - 4 = 0 → y1 = lgx1 = 1, y2 = lgx2 = - 4 →
x1 = 10, x2 = 10-4 ;
34) Quadrieren ergibt: x2 + 21 = (x + 1)2 → 2x = 20 → x = 10 ;
35) log2x + log4x + log16x = log2x + (1/2)log2x + (1/4)log2x = (7/4)log2x = 7 → log2x = 4 →
x = 16 ;
37) a = 3, b = 3, c = f(12) = 122 - 5 = 139 → d = abc = 3 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 139 = 1251 ;
40) a1 = 10, b1 = 30, c1 = 20 → V = abc = a1a2a3 cm3 = 6000 cm3 ;
41) Mit sin(180° + α) = - sinα und sin(180° - α) = sinα ergibt sich a = (9 ⋅ sin270°)2 = (9 ⋅ (- 1))2 = 81 ;
43) 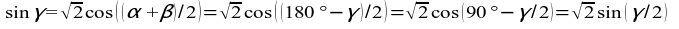 →
→ 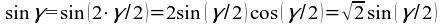 →
→ 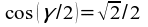 → γ = 90° ;
→ γ = 90° ;
44) a1 = 7 ⋅ (- 1)2 = 7, b1 = 13 → A = 7 ⋅ 13 cm2 = 91 cm2 ;
46) g = 11 + 0 + 1 = 12 ;
47) f ' (x) = 9x2 + 12x - 10 → f ' (1) = 9 + 12 - 10 = 11 ;
49) f ' (x) = 3 - (x3 - 3(x + 3)x2)/x6 = 3 + (2x + 9)/x4 → f ' (- 1) = 10 ;
50) 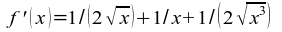 → f ' (1/9) = 24 ;
→ f ' (1/9) = 24 ;
53) y = f(x) = x3 + x2 - x + 15 → f ' (x) = 3x2 + 2x - 1, f '' (x) = 6x + 2 → f '' (12) = 74 ;
54) f ' (x) = cos2x - sin2x → f ' (0) = 1 = tanα → α = 45° ;
56) f ' (x) = 3x2 - 42x + 120 = 0 → x2 - 14x + 40 = 0 → x1 = 10, x2 = 4 → x1x2 = 40 (f '' (x) = 6x - 42 →
f '' (10) = 18 > 0, f '' (4) = -18 < 0) ;
58) f(x) = ax3 + bx2 + cx + d, f ' (x) = 3ax2 + 2bx + c → f (0) = d = 2, f (1) = a + b + c + 2 = 6, f ' (2) = 12a + 4b + c = 18, f ' (3) = 27a + 6b + c = 35
→ a = 1, b = 1, c = 2, f (x) = x3 + x2 + 2x + 2 → f (4) = 90;
59) Ansatz y = f(x) = ax2 + bx + c → f ' (x) = 2ax + b, f '' (x) = 2a → f (0) = c = - 2, f ' (1) = 2a + b = 2, f '' (2) = 2a = 10 → a = 5, b = -8, c = - 2,
f (x) = 5x2 - 8x - 2 → f (5) = 83 ;
61) Die beiden Rechteckseiten seien x (an der Mauer angrenzend) und y → 2x + y = 16, Fläche A = xy = x(16 - 2x), A ' = dA/dx = 16 - 4x = 0 → x = 4, y = 8 → Amax = 4 ⋅ 8 = 32 (A '' = - 4 < 0 → Maximum) ;
62) H/(r - R) = h/r, H = h(r - R)/r (R Grundkreisradius, H Höhe des Kreiszylinders) → V = VZyl = π R2H = πR2h(r - R)/r, V ' = dV/dR = 2 π hR -
3πhR2/r = 0 → R(3R - 2r) = 0 → R = 2r/3 = 3 cm, H = 3 cm (da R > 0) → Längsquerschnitt 2HR = 18 cm2 ;
63) Querschnittsfläche A = (x + a)h/2 (x und a Parallelseiten - dabei x Breite eines Brettes - und h Höhe des Trapezes), h = x ⋅ sinα, b = x ⋅ cosα, a = x + 2b = x + 2xcosα → A = (x + a)h/2 = (1 + cosα)sinα ⋅ x2, A ' = dA/dα = (cosα + cos2α - sin2α) ⋅ x2 = 0 → 2cos2α + cosα - 1 = 0 → cosα = - 1 (entfällt: 0< α <90°) und cosα = 1/2 → α = 60° .
Senkrecht:
1) V = Alter des Vaters, P = Alter von Peter: V + t = 2(P + t) → 33 + t = 2(10 + t) → t = 13 (Jahre) ;
2) (31 - x)/20 = 1 → x = 11 ;
3) Zweipunktegleichung: (y - 0)/(x - 0) = (11 - 0)/(1/11 - 0) → y = 121x → m = 121 ;
5) y = - x/12 → Ansatz für g: y = - x/12 + n, P(0, 12) einsetzen: n = 12 → y = - x/12 + 12 = 0 → x = 144 ;
7) s = v ⋅ t = 126 km/h ⋅ 6s = 126 ⋅ 103m ⋅ 6s/3600s = 210 m ;
8) m = ρ ⋅ V = (3000 kg/m3) ⋅ (37 cm3) = 3 ⋅ 106 ⋅ 37 g cm3/106cm3 = 111 g ;
12) x/5 + x/7 + x/11 = (77 + 55 + 35)x/385 = 167x/385 = 167 → x = 385 ;
14) 6903/x - 1 = 2301/x + 1 → (6903 - 2301)/x = 2 → x = 4602/2 = 2301 ;
15) x/83 + 68 = x/15 → x/15 - x/83 = (83 - 15)x/1245 = 68 → x = 1245 ;
20) x2 - 10x + 21 = 0 → x1 = 7, x2 = 3 → P = 7 ⋅ 3 = 21 ;
21) f(10) = 1,5 ⋅ 102 - 15 ⋅ 10 + 10 = 10 ;
23) x2 - 4x + 4 = (x - 2)2 = 0 → a = b = 2, c = 7, y = f(x) = 2x2 - 2x - 7 → f(7) = 2 ⋅ 72 - 2 ⋅ 7 - 7 = 77 ;
24) a - b = 46, 46a + b = 1 → a = 1, b = - 45, f(x) = x2 - 45x + 44 = 0 → x1 = 1, x2 = 44 ;
27) h = gt2/2 = 9,81 ⋅ 6,32/2 m ≈ 194,68 m ≈ 195 m = 19500 cm ;
28) 0 = f(10) = 104 - 189 ⋅ 10 - c → c = 10000 - 1890 = 8110 ;
29) 2n(n2 + 1) = 5n2 → n1 = 0, für n ≠ 0 gilt 2(n2 + 1) = 5n bzw. n2 - 5n/2 + 1 = 0 → n2 = 2, n3 = 1/2
Lösung (ganzzahlig, in geordneter Reihenfolge): n1 = 0, n2 = 2 (Schreibweise: 02) ;
31) 1 = f(0) = lg( c ⋅ (1 - 0)/(7 - 0)) = lg( c/7 ) → 101 = c/7 → c = 70 ;
34) 3x - 2y = 7, x + 2y = 29 → x = 9, y = 10 → a = x2 + y2 = 92 + 102 = 181 ;
36) f(8) = 38 - 111 = 6450 ;
37) Durch Quadrieren ergibt sich: 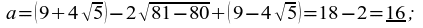
38) x0 = 11 → f(11) = 211 = 2048 ;
39) Quadrieren von 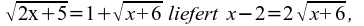 abermaliges Quadrieren liefert x2 - 8x -20 = 0 → x1 = -2, x2 = 10 ;
abermaliges Quadrieren liefert x2 - 8x -20 = 0 → x1 = -2, x2 = 10 ;
42) 1 + lgx ≥ 0 (x ≥ 1/10) → | 1 + lgx | = 1 + lgx = 3 → lgx = 2 → x = 102 = 100 (Der Fall 1 + lgx < 0 bzw. 0 < x < 1/10 liefert
x = 10-4.) ;
43) 2x - 99 = | x + 900 | ≥ 0 → x ≥ 99/2 → x + 900 ≥ 0 → | x + 900 | = x + 900 = 2x - 99 → x = 999 ;
45) 2x+1 - 2x - 2x-1 = 4 ⋅ 2x-1 - 2 ⋅ 2x-1 - 2x-1 = (4 - 2 - 1)2x-1 = 2x-1 = 512 → x - 1 = 9 → x = 10 ;
46) 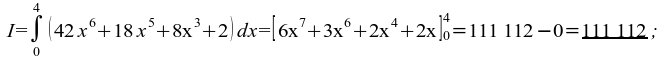
48) a = tan(arccos0,1)/sin(arccos0,1) = sin(arccos0,1)/(sin(arccos0,1) ⋅ cos(arccos0,1)) = 1/cos(arccos0,1) = 1/0,1 = 10 ;
51) x = - 3 ist Nullstelle von f(x) in (-4, -2) → 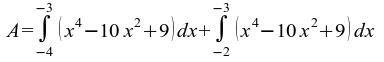 Stammfunktion F von f: F(x) = x5/5 - 10x3/3 + 9x → A = ( F(-3) - F(-4) ) + ( F (-3) - F(-2) ) = 2 ⋅ F(-3) - F(-2) - F(-4) = 2 ⋅ 72/5 - 34/15 - (- 412/15) = 810/15 = 54 (LE2) ;
Stammfunktion F von f: F(x) = x5/5 - 10x3/3 + 9x → A = ( F(-3) - F(-4) ) + ( F (-3) - F(-2) ) = 2 ⋅ F(-3) - F(-2) - F(-4) = 2 ⋅ 72/5 - 34/15 - (- 412/15) = 810/15 = 54 (LE2) ;
52) 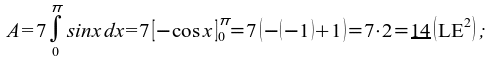
53) Grenzen: y = 111 = 37x2/768 → x1 = - 48, x2 = 48 → 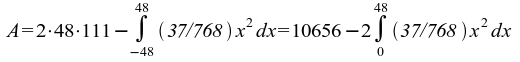
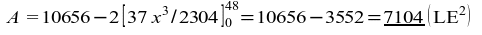 ;
;
55) 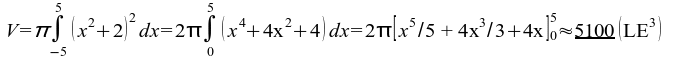 ;
;
57) f(x) = x4/12 - x3/6 + x + 1, f ' (x) = x3/3 - x2/2 + 1, f '' (x) = x2 - x, f ''' (x) = 2x - 1 → f '' (x) = x2 - x = x(x - 1) = 0 → x1 = 0, x2 = 1, f ''' (0) = - 1 ≠ 0, f ''' (1) = 1 ≠ 0 → Ergebnis (Wendepunkt-Abszissen in geordneter Reihenfolge): 01 ;
58) 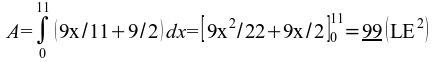 ;
;
60) f(9)(x) = 9 ⋅ 8 ⋅ 7 ⋅ 6 ⋅ 5 ⋅ 4 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 1 = 9! = 362880 ;
61) 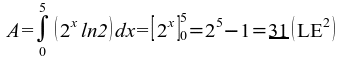 .
.
Kontrollmöglichkeit:
Bei richtiger Auflösung des Kreuzzahlrätsels ergeben sich in den Kästchen mit den zweistelligen Primzahlnummern 11-13-17-19-23-29-31-37-41-43-47-53-59-61 die
Ziffern 1-5-4-1-7-0-7-1-8-9-1-7-8-3 und damit mittels geeigneter Punktierung die Lebensdaten von Leonhard Euler: 15.4.1707 bis 18.9.1783.